BIND 9 DNS Cache Poisoning (CVE-2025-40778)
Published on 03-Nov-2025 16:00:00
Executive Summary
A high-severity cache-poisoning vulnerability (CVE-2025-40778, CVSS 8.6) in BIND (Berkeley Internet Name Domain) 9 resolvers can allow remote attackers to inject forged DNS records into resolver caches. All organizations operating BIND 9 resolvers in Bangladesh (ISPs, data centers, government, enterprises) must upgrade to ISC (Internet Systems Consortium) patched releases 9.18.41, 9.20.15, 9.21.14 (or S1 variants) immediately. If you cannot patch immediately, restrict recursion to trusted networks, enable DNSSEC validation where possible, and monitor DNS logs for anomalous answers.
Vulnerability Summary
- BIND 9 resolvers are too lenient when accepting records from answers, allowing an attacker to inject forged resource records (unsolicited RRs) into a resolver cache during normal queries. This can cause future lookups to be resolved with forged (malicious) answers.
- Affected versions (per ISC): BIND 9.11.0 → 9.16.50, 9.18.0 → 9.18.39, 9.20.0 → 9.20.13, 9.21.0 → 9.21.12 (and corresponding S1 preview builds).
- CVSS: ISC / CNA score 8.6 (High) as per NVD (National Vulnerability Database), NIST.
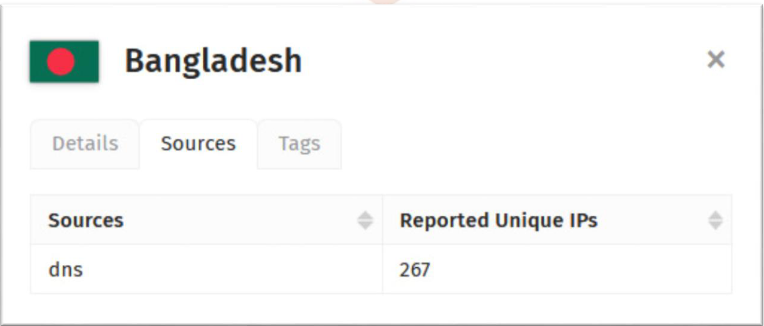
Figure: Footprint in Bangladesh