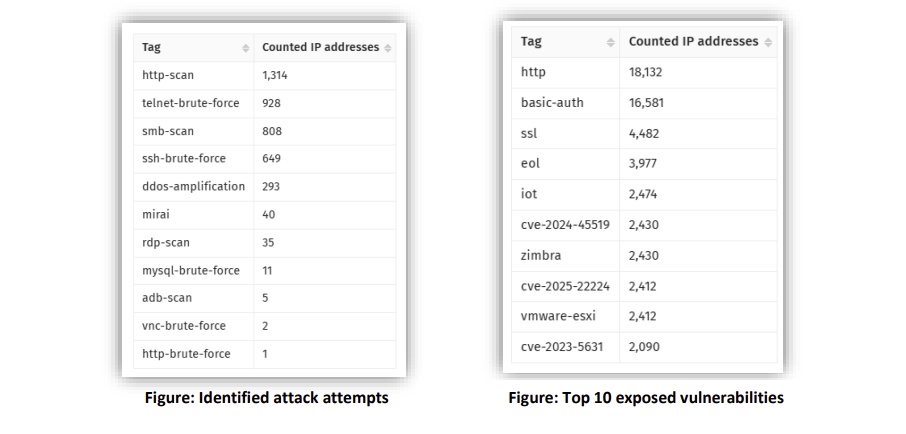
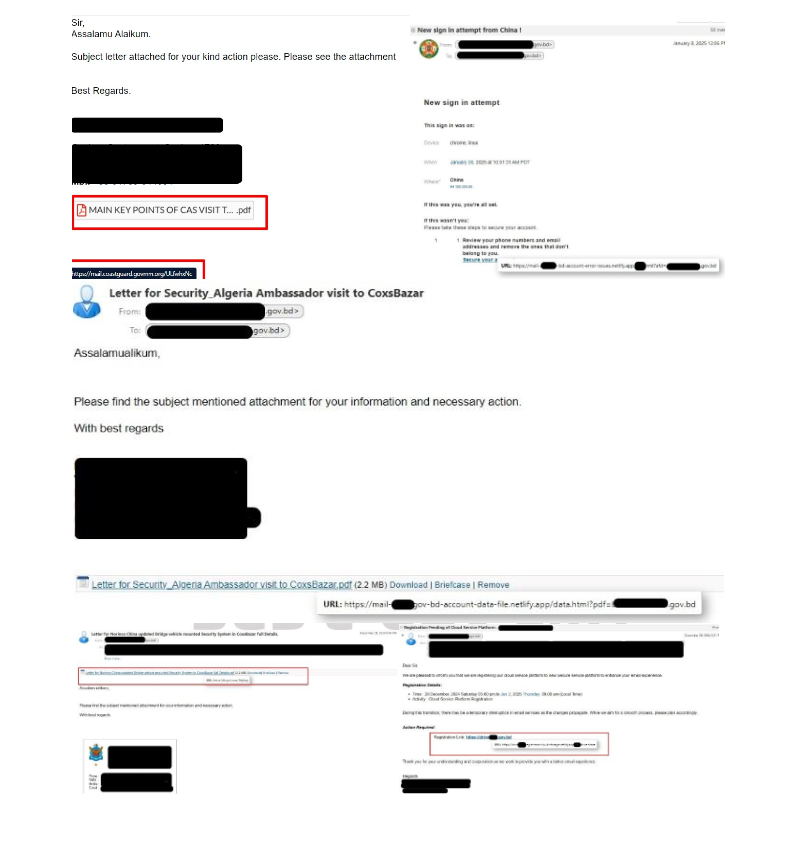
9 Android Apps On Google Play Caught Distributing AlienBot Banker and MRAT Malware [thehackernews]
by CIRT Team
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a new malware dropper contained in as many as 9 Android apps distributed via Google Play Store that deploys a second stage malware capable of gaining intrusive access to the financial accounts of victims as well as full control of their devices.
“This dropper, dubbed Clast82, utilizes a series of techniques to avoid detection by Google Play Protect detection, completes the evaluation period successfully, and changes the payload dropped from a non-malicious payload to the AlienBot Banker and MRAT,” Check Point researchers Aviran Hazum, Bohdan Melnykov, and Israel Wernik said in a write-up published today.
The apps that were used for the campaign include Cake VPN, Pacific VPN, eVPN, BeatPlayer, QR/Barcode Scanner MAX, Music Player, tooltipnatorlibrary, and QRecorder. After the findings were reported to Google on January 28, the rogue apps were removed from the Play Store on February 9.https://7b791e1a7b7046c288d5b46b897f238c.safeframe.googlesyndication.com/safeframe/1-0-37/html/container.html
Malware authors have resorted to a variety of methods to bypass app store vetting mechanisms. Whether be it using encryption to hide strings from analysis engines, creating rogue versions of legitimate apps, or crafting fake reviews to lure users into downloading the apps, fraudsters have hit back at Google’s attempts to secure the platform by constantly developing new techniques to slip through the net.
Equally popular are other methods like versioning, which refers to uploading a clean version of the app to the Play Store to build trust among users and then sneakily adding unwanted code at a later stage via app updates, and incorporating time-based delays to trigger the malicious functionality in an attempt to evade detection by Google.
Reference: https://thehackernews.com/2021/03/9-android-apps-on-google-play-caught.html